Introduction to Variant analysis
Contributors
Authors:

 Bérénice Batut
Bérénice Batut

 Yvan Le Bras
Yvan Le Bras


last_modification Last modification: Nov 25, 2022
What is Exome sequencing?
Exome sequencing
= Whole exome sequencing (WES or WXS)
Sequencing of all expressed protein-coding genes in a genome
Exome in Humans
- ~180,000 exons
- 1% of the human genome
- ~30 million base pairs
Goal of exome sequencing
Identify genetic variation that is responsible for both Mendelian and common diseases without the high costs associated with whole-genome sequencing
Exome sequencing is the most efficient way to identify the genetic variants in all of an individual’s genes
Limits
Exome sequencing can not identify genetic variation in
- All genes
- Mitochondrial genes
- “Structural variants”
- Triplet repeat disorders
- Other copy number variants
- Introns
- “Uniparental disomy”
- Control sequences
- Epigenetic changes
- Gene-gene (epistatic) interactions
2 tutorials for training on exome sequencing data analysis
Same goal
Identify and annotate genetic variants in a family with two parents and a child exome data
Similar data analysis approach
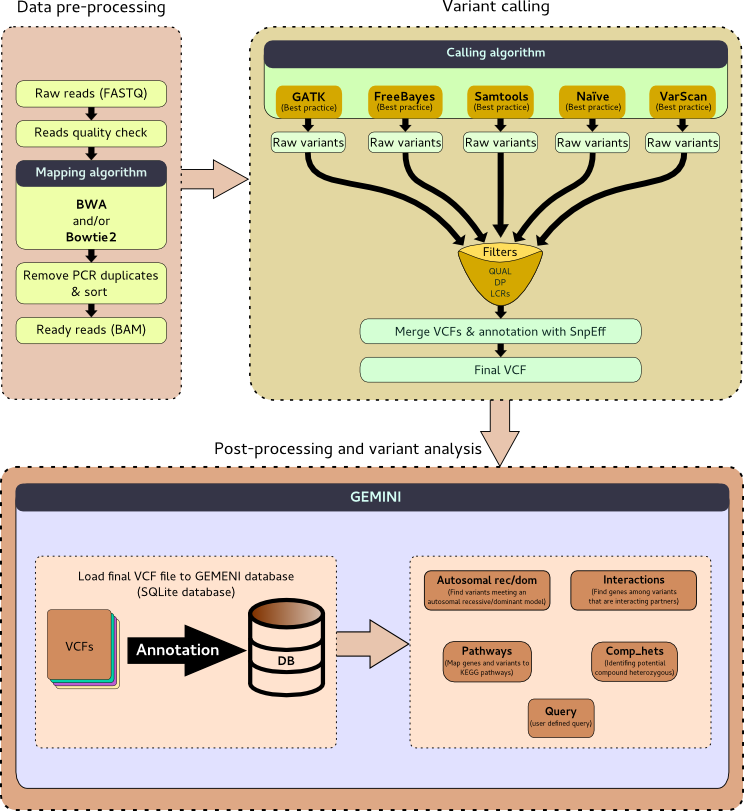
### 2 tutorials
Thank you!
This material is the result of a collaborative work. Thanks to the Galaxy Training Network and all the contributors! This material is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
This material is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.